how does an electric train work
Electric locomotives, also known as electric trains, are a marvel of modern engineering. These incredible machines offer a sustainable and efficient means of transportation, propelling us into the future with clean energy solutions. In this post, we will delve into the inner workings of electric locomotives and explore how they operate seamlessly on our railway systems.
How Does an Electric Locomotive Work?

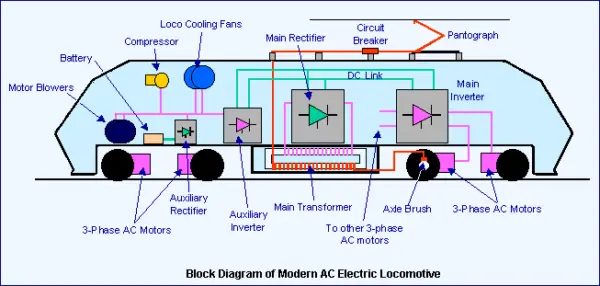
Electric locomotives are powered by electric motors that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the train forward. The key component of an electric locomotive is the pantograph, which connects to the overhead power lines and collects the electrical current needed to power the train.
Once the electrical current is collected, it is directed to the locomotive's electrical system, where it is distributed to various subsystems and components. This includes powering the traction motors, which are responsible for driving the train's wheels.
The traction motors in an electric locomotive are similar to the engines found in conventional diesel locomotives. However, instead of being driven by diesel fuel, they are powered by electricity. This eliminates the need for combustion and significantly reduces both noise and air pollution.
Electric locomotives rely on a sophisticated control system to regulate the power distribution from the electrical system to the traction motors. This system continuously monitors the train's speed, acceleration, and other factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
The Benefits of Electric Locomotives
The shift towards electric locomotives offers numerous advantages over traditional combustion-powered trains. First and foremost, electric trains are much more environmentally friendly. They produce zero direct emissions, reducing our carbon footprint and helping to combat climate change.
Furthermore, electric trains are remarkably efficient. Electric motors have a higher energy conversion rate compared to internal combustion engines, resulting in lower energy consumption and operating costs. This increased efficiency also leads to quieter operation, contributing to a more pleasant travel experience for passengers and reduced noise pollution for nearby communities.

Electric locomotives also offer improved acceleration and faster response times compared to their diesel counterparts. This allows for a smoother and more reliable travel experience, particularly in urban areas where frequent stops and starts are common.
Another benefit of electric locomotives is their regenerative braking system. When the train brakes, the traction motors reverse their operation, acting as generators that convert the kinetic energy into electrical energy. This energy is then fed back into the electrical system and can be used to power other trains or stored for future use. This regenerative braking system not only enhances the overall energy efficiency of electric trains but also reduces wear and tear on braking components, extending their lifespan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric locomotives are the future of sustainable and efficient railway transportation. Through the use of electric motors, sophisticated control systems, and regenerative braking technology, these trains offer numerous benefits over traditional combustion-powered trains. From reduced emissions and lower operating costs to improved acceleration and a quieter travel experience, the advantages of electric locomotives are clear.
As we continue to embrace clean energy solutions and strive for a greener future, electric locomotives are playing a vital role in revolutionizing the way we travel. Their impressive performance and environmentally conscious design make them a compelling choice for railways around the world.

Post a Comment for "how does an electric train work"